Our latest theory work on quantum spatiotemporal optical vortices is now published in New Journal of Physics. Here, we develop a quantum theory for STOVs with an arbitrary tilt, extending beyond the paraxial limit. We demonstrate that quantum STOV states, such as Fock and coherent twisted photon pulses, display non-vanishing longitudinal OAM fluctuations that are absent in conventional monochromatic twisted pulses.
Read full article at: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1367-2630/ad692a
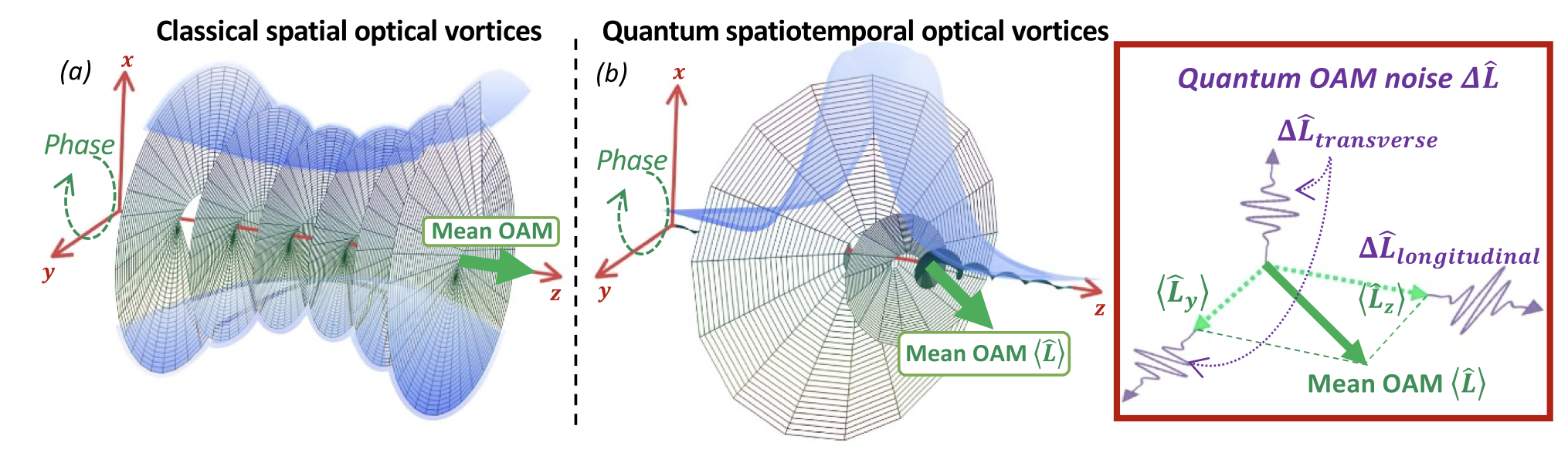
Abstract: Spatiotemporal Optical Vortices (STOVs) are structured electromagnetic fields propagating in free space with phase singularities in the space-time domain. Depending on the tilt of the helical phase front, STOVs can carry both longitudinal and transverse orbital angular momentum (OAM). Although STOVs have gained significant interest in the recent years, the current understanding is limited to the semi-classical picture. Here, we develop a quantum theory for STOVs with an arbitrary tilt, extending beyond the paraxial limit. We demonstrate that quantum STOV states, such as Fock and coherent twisted photon pulses, display non-vanishing longitudinal OAM fluctuations that are absent in conventional monochromatic twisted pulses. We show that these quantum fluctuations exhibit a unique texture, i.e. a spatial distribution which can be used to experimentally isolate these quantum effects. Our findings represent a step towards the exploitation of quantum effects of structured light for various applications such as OAM-based encoding protocols and platforms to explore novel light–matter interaction in 2D material systems.
